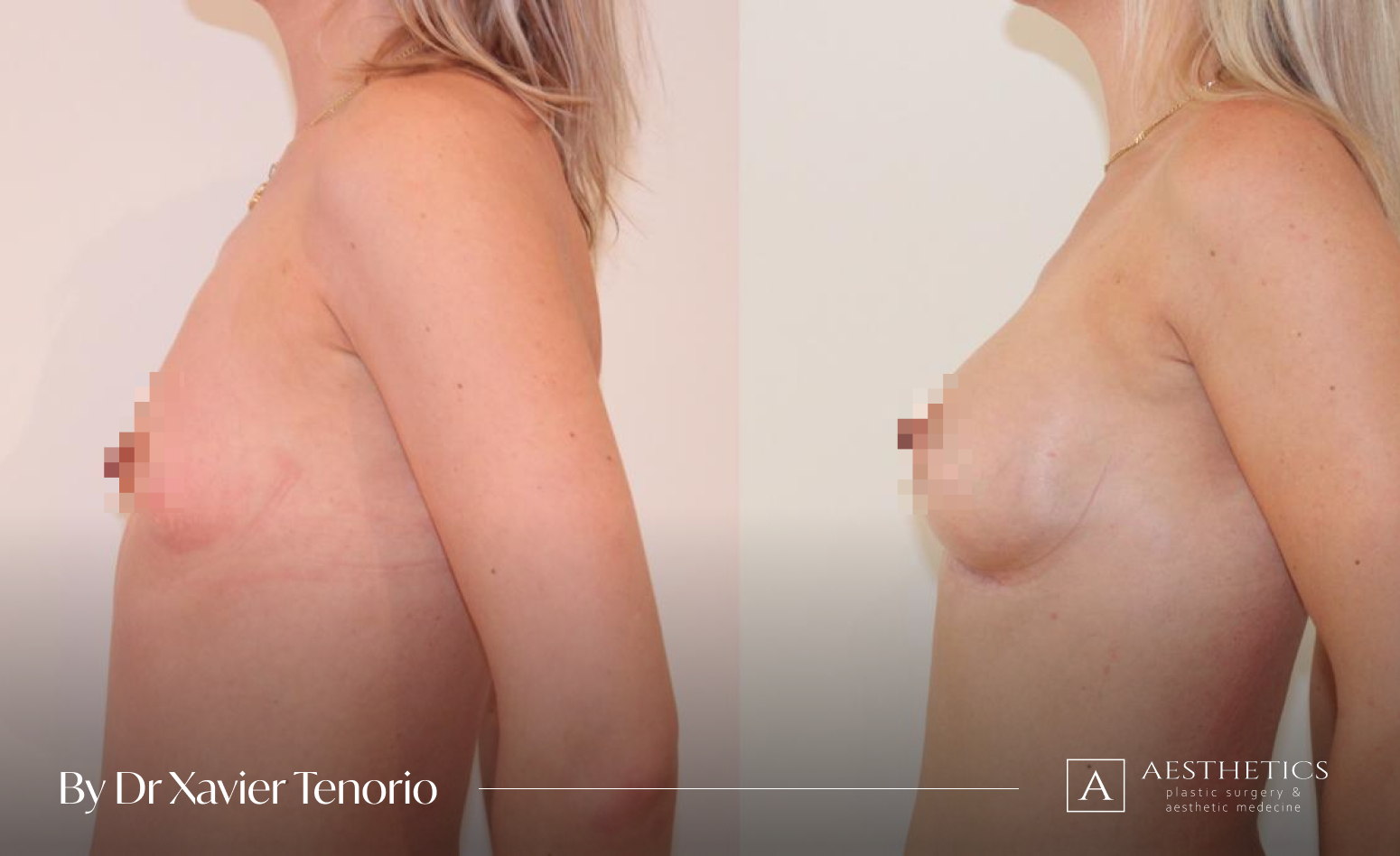
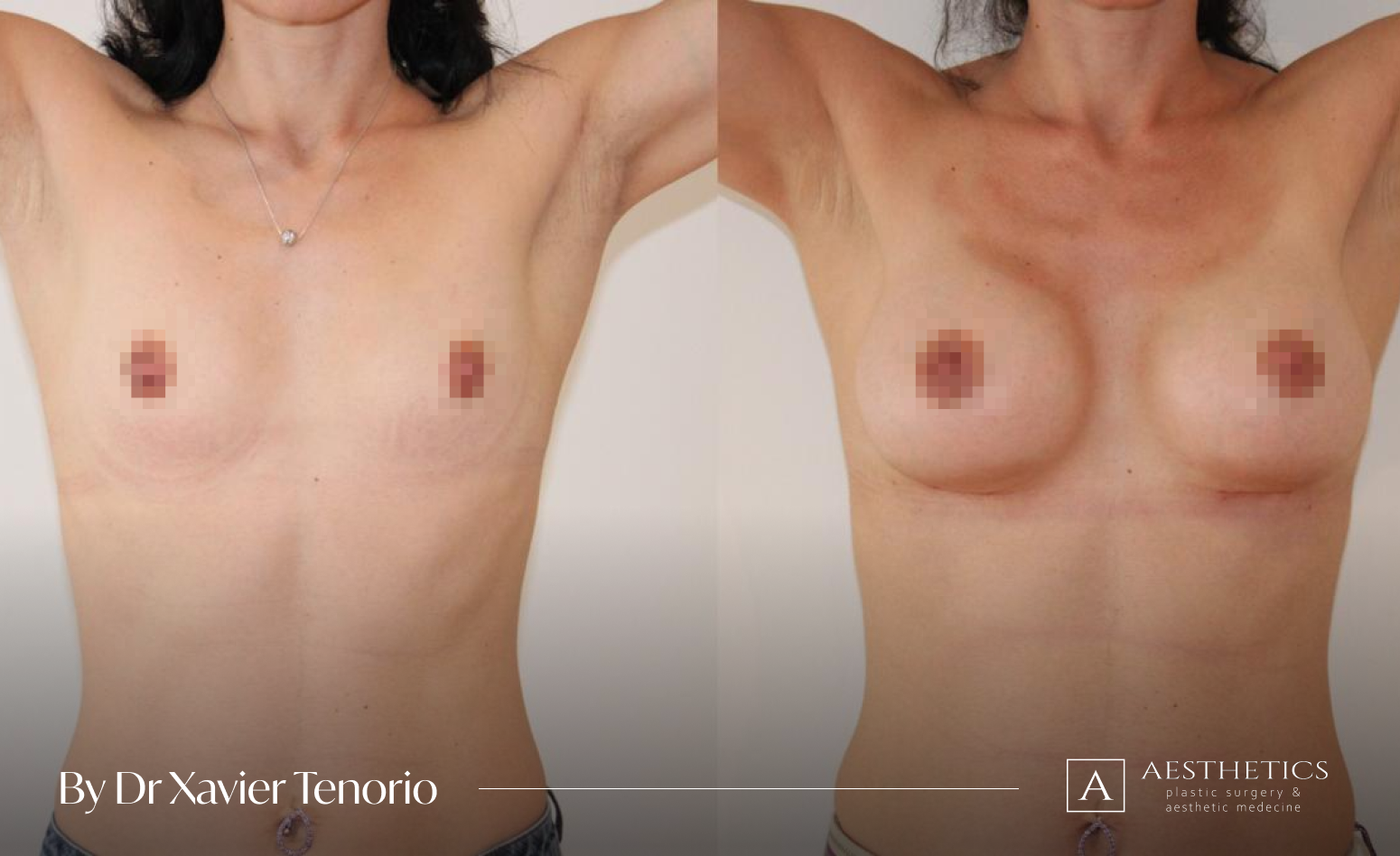
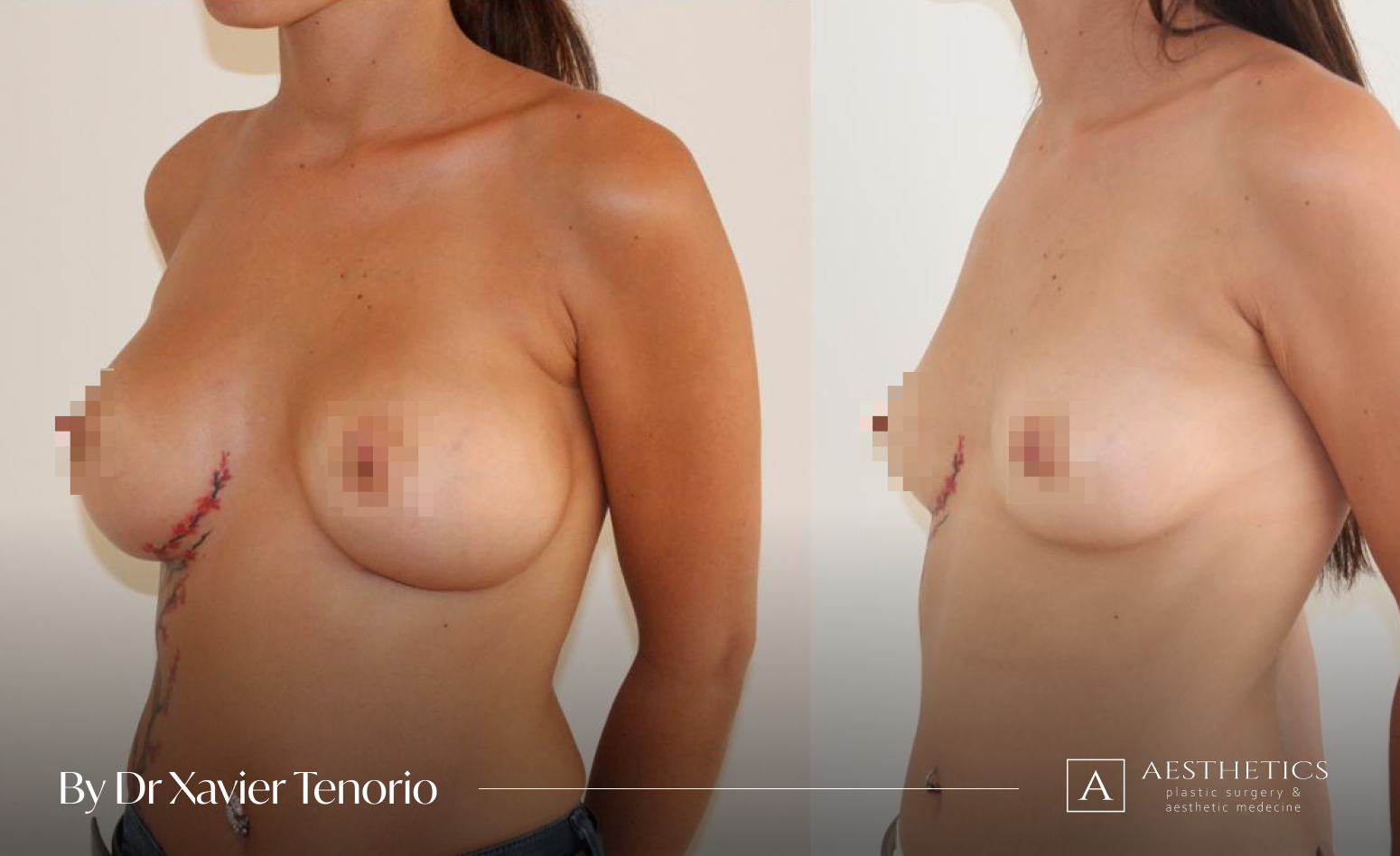
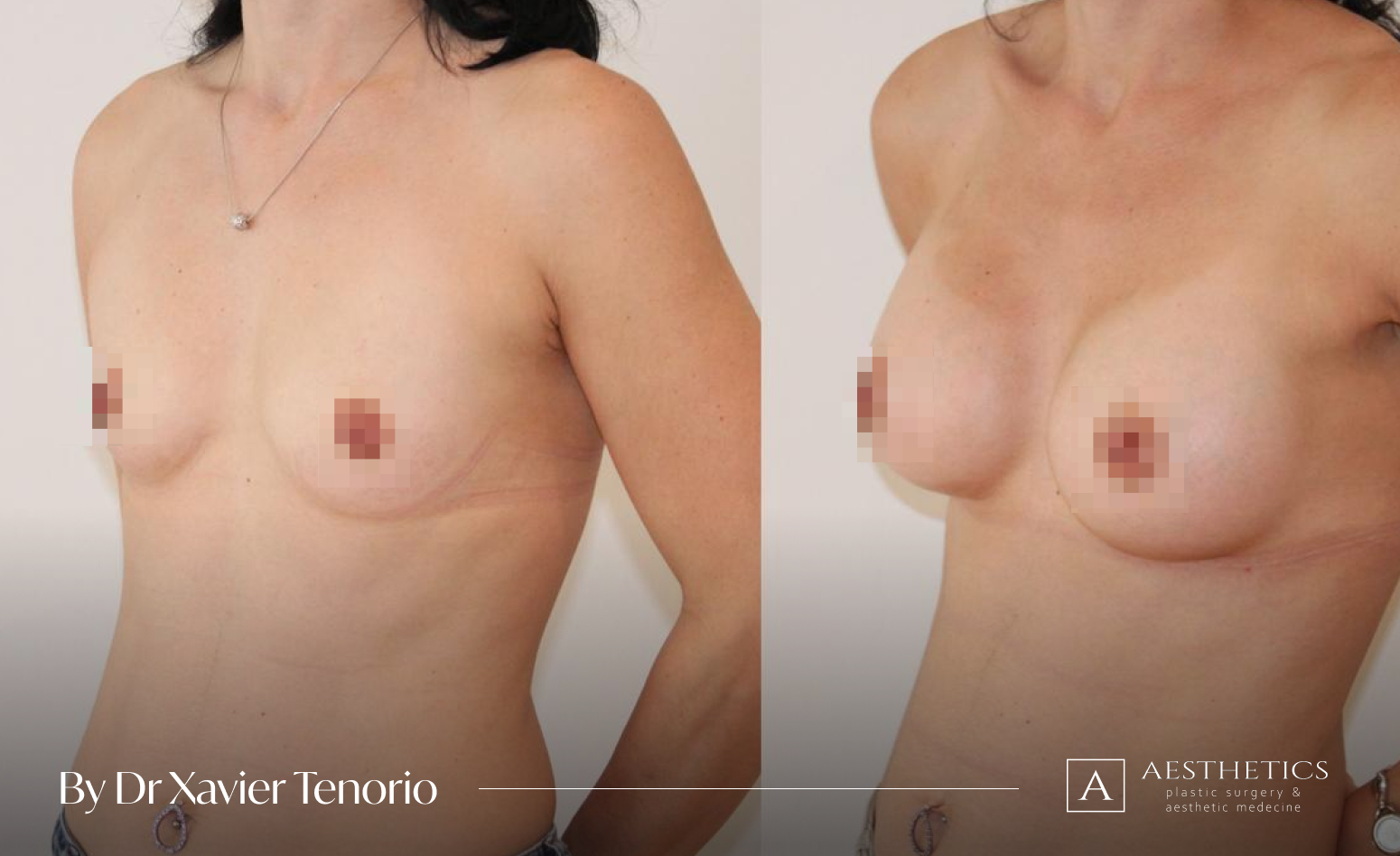
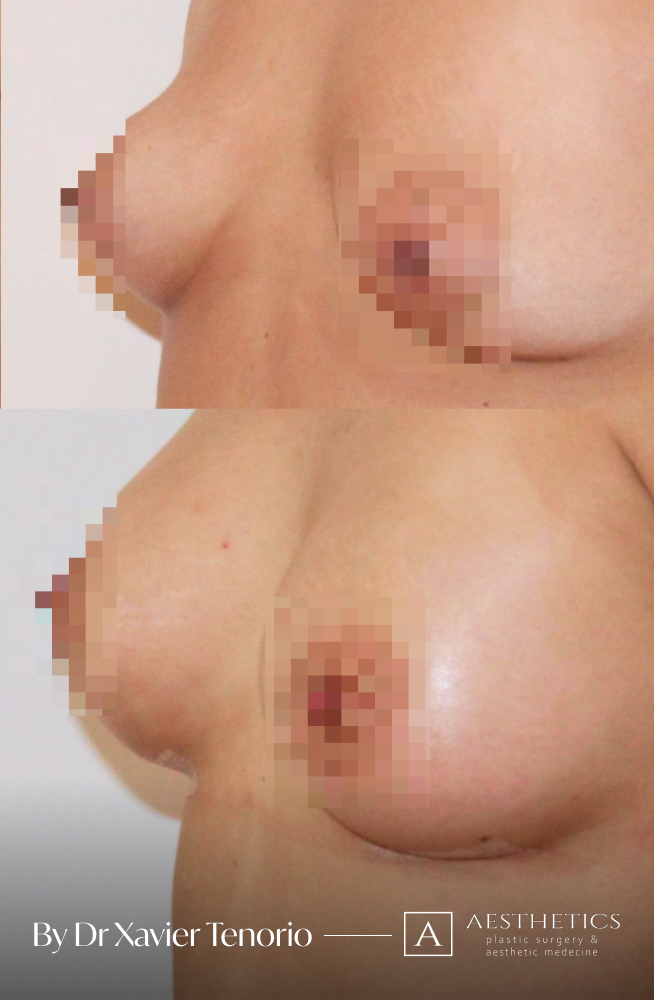
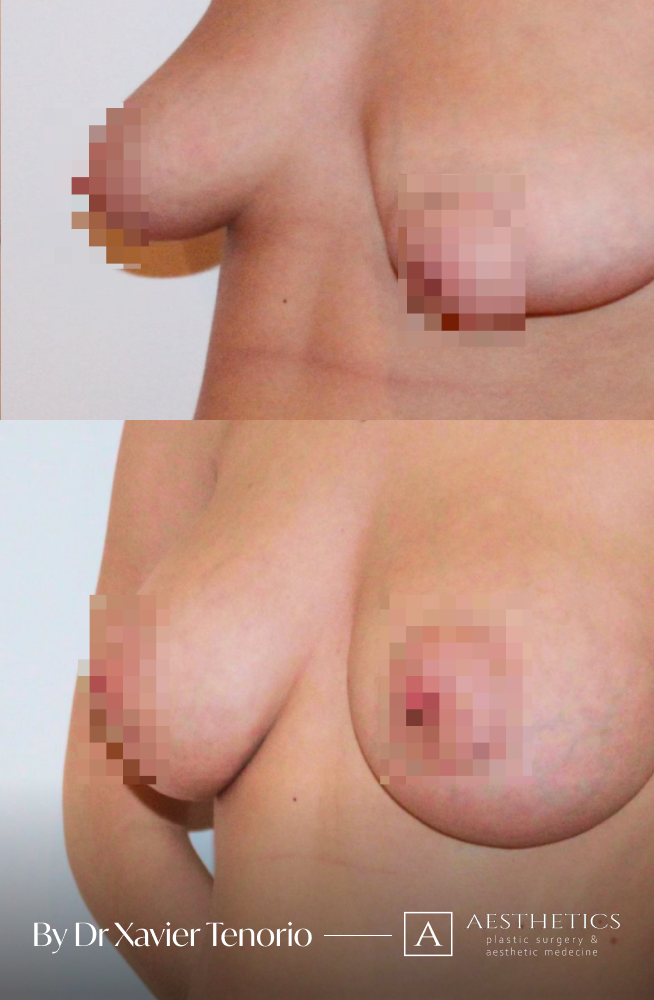
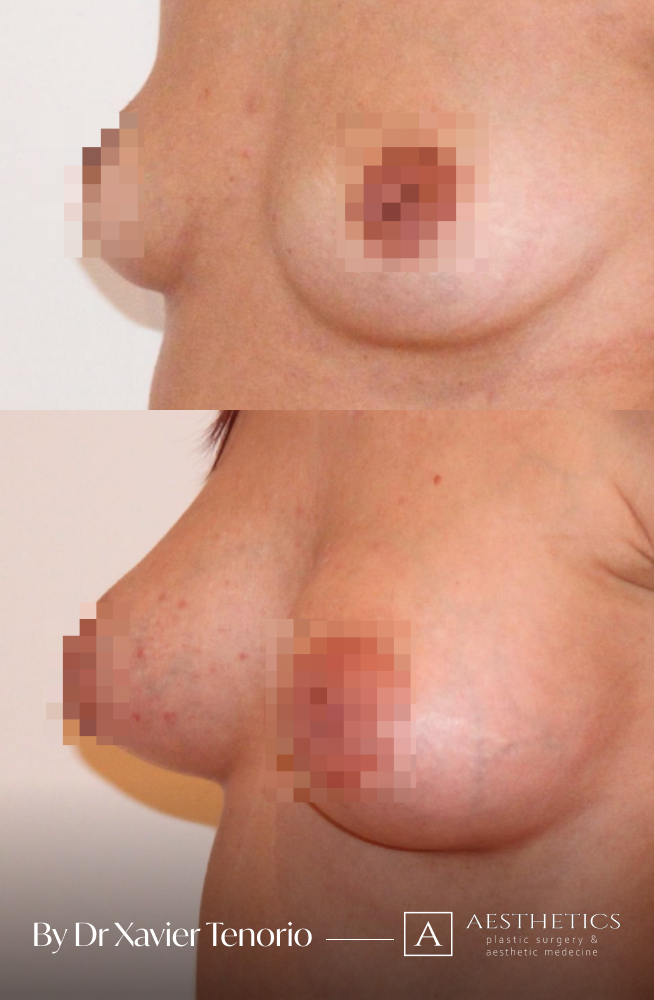
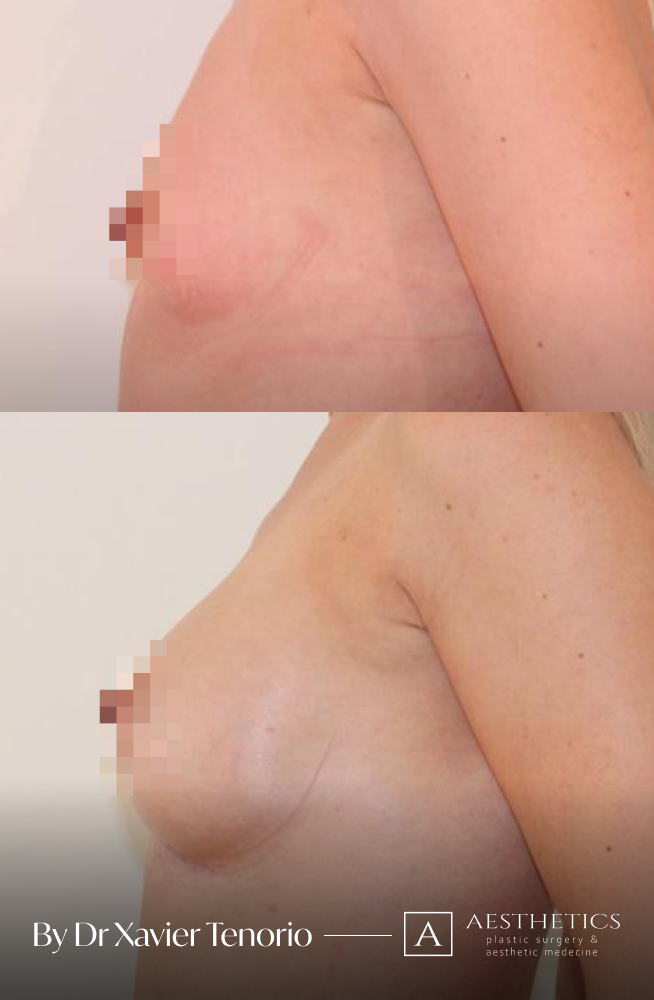
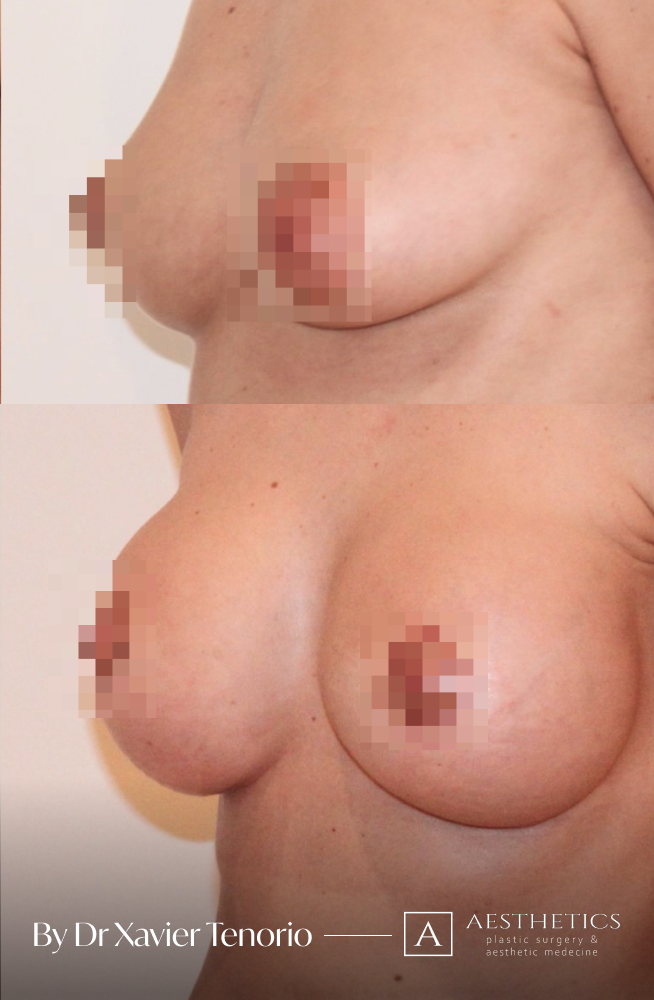
Specialist in breast augmentation : Dr Xavier Tenorio
Experience of breast augmentation :
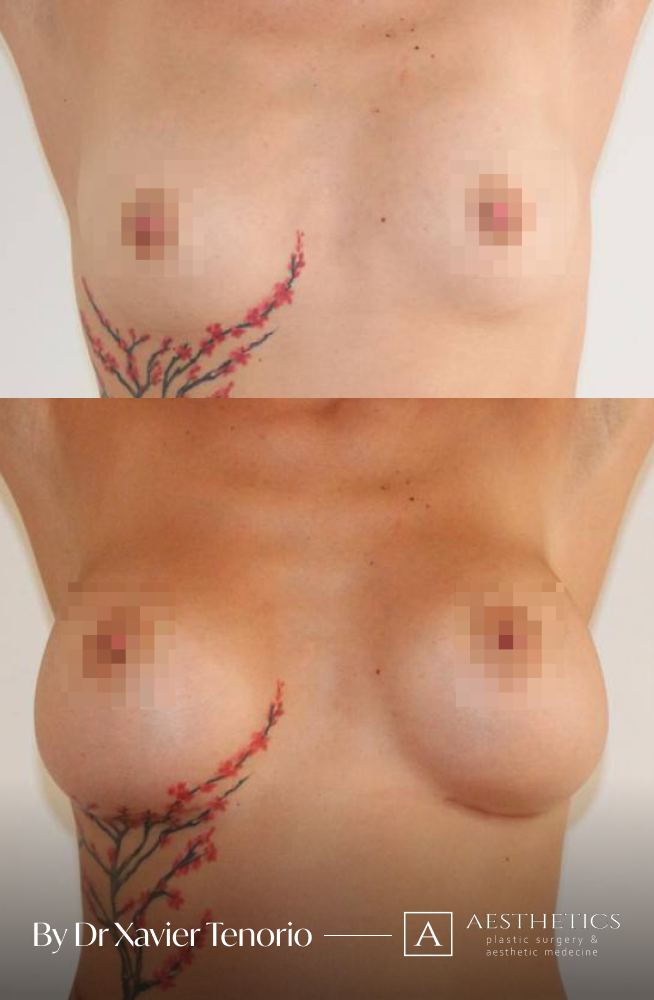
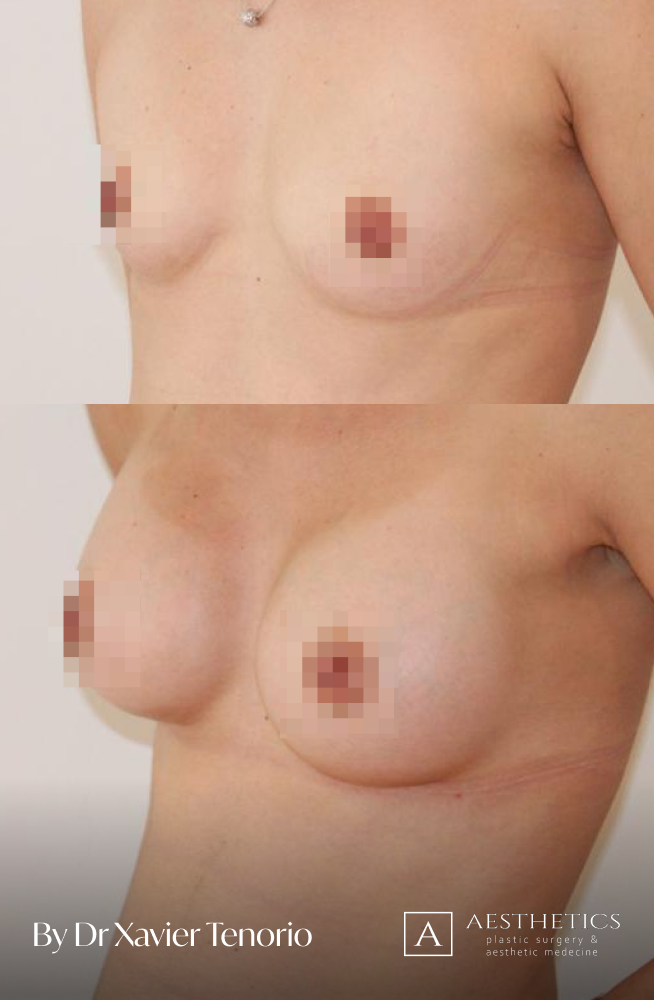
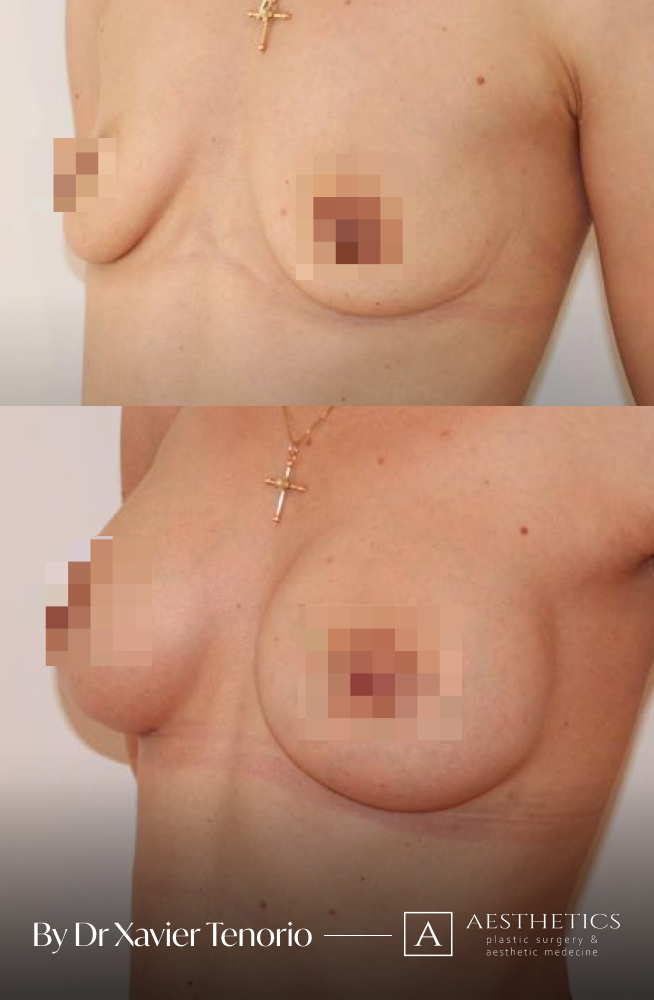
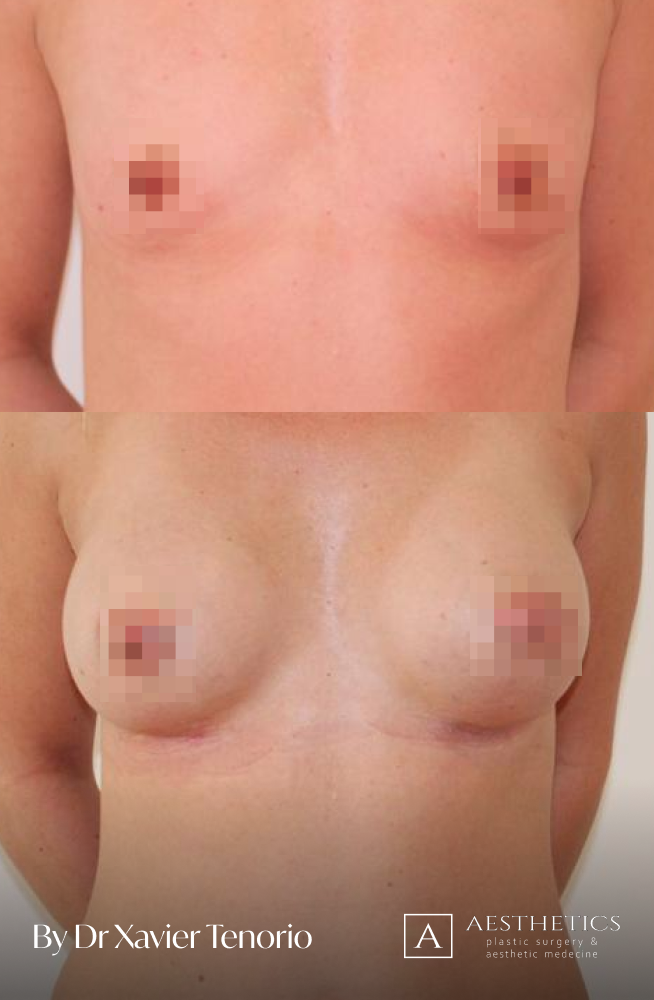
I have performed more than 1,000 breast augmentations since the start of my career. Each patient has been able to benefit from my unique expertise in Europe, enabling me to offer natural and above all subtle results for breasts that are quite simply beautiful and magnificent. Technique in cosmetic surgery is one thing, but experience is what makes it possible to offer a definitive result that lives up to your expectations just a few weeks after breast augmentation surgery using prostheses. Your joy is my vision of perfection! It’s more than a phrase, it’s the result of exceptional skill at your service. Dr Xavier Tenorio
Breast Augmentation in Geneva
Are you looking for effective breast surgery to achieve that natural breast shape that fits perfectly in your bra?
- This aesthetic procedure is ideal for any woman concerned about her appearance who wants to boost her self-confidence.
- If you have sagging, uneven, asymmetrical, underdeveloped, or too small breasts, you can undergo breast augmentation in Geneva to regain a “sexy” aesthetic appearance and improve your self-confidence by enhancing your femininity.
- Here you will find answers to questions about implant types, augmentation methods, pain, cost, recovery time, and more.
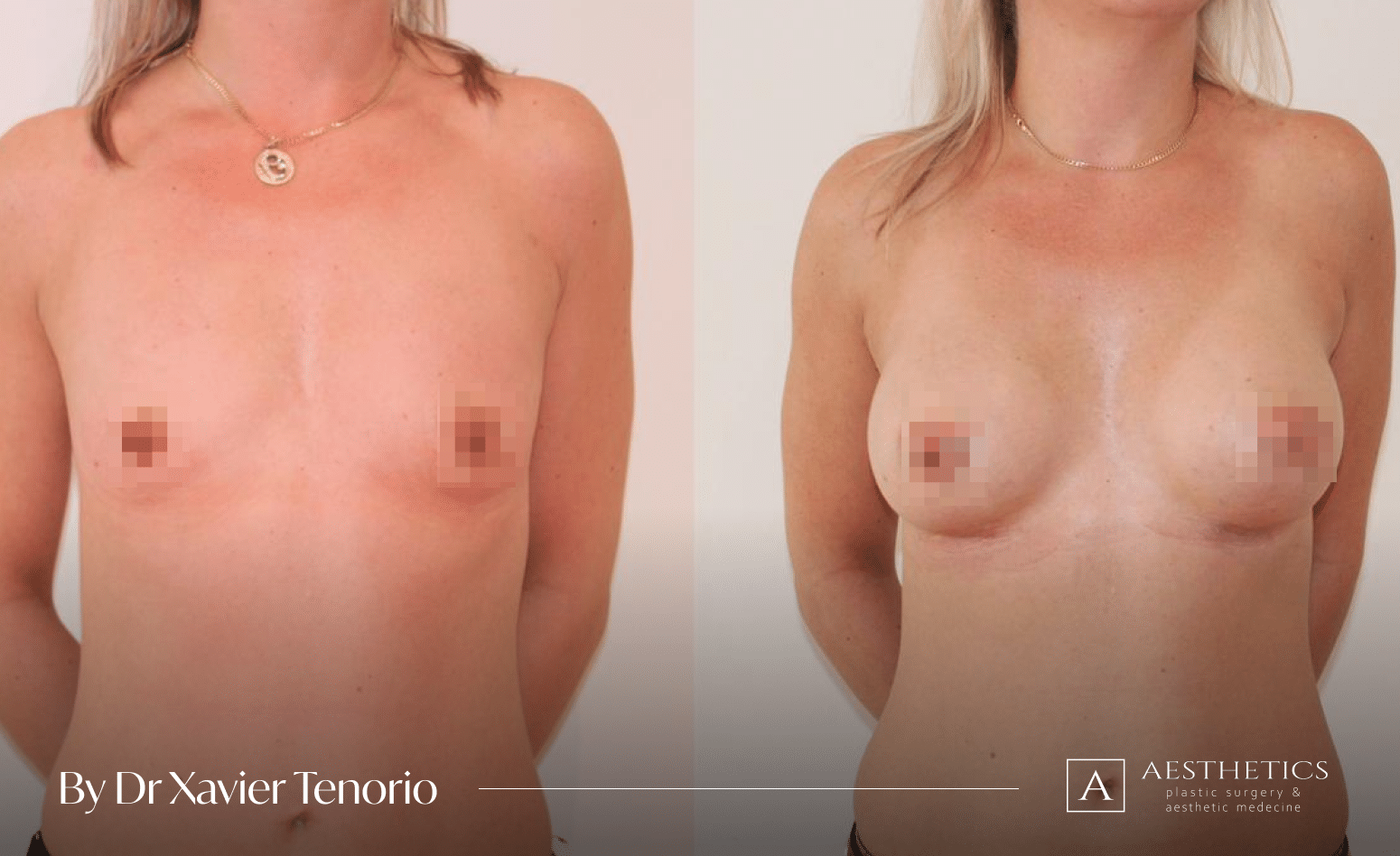
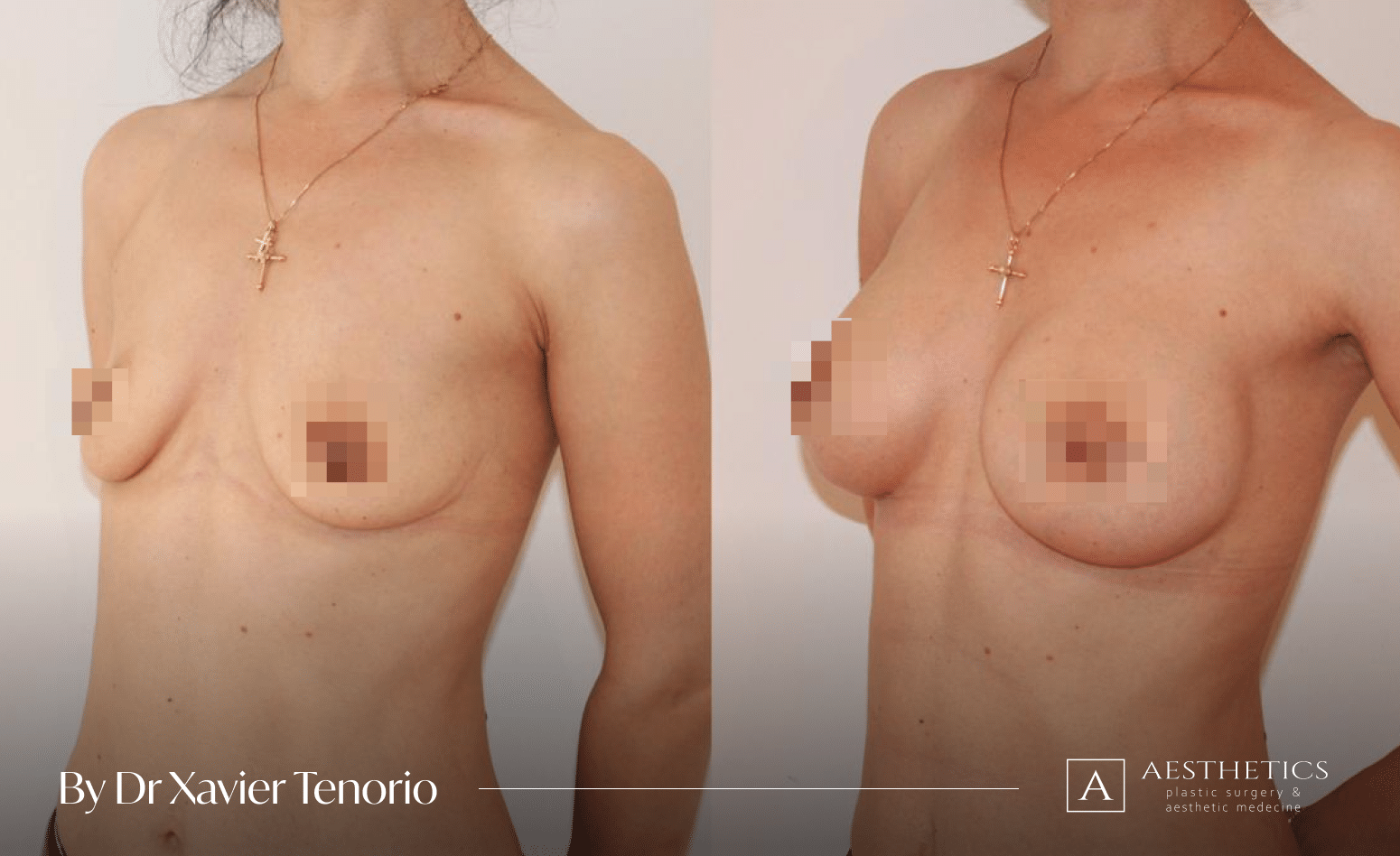
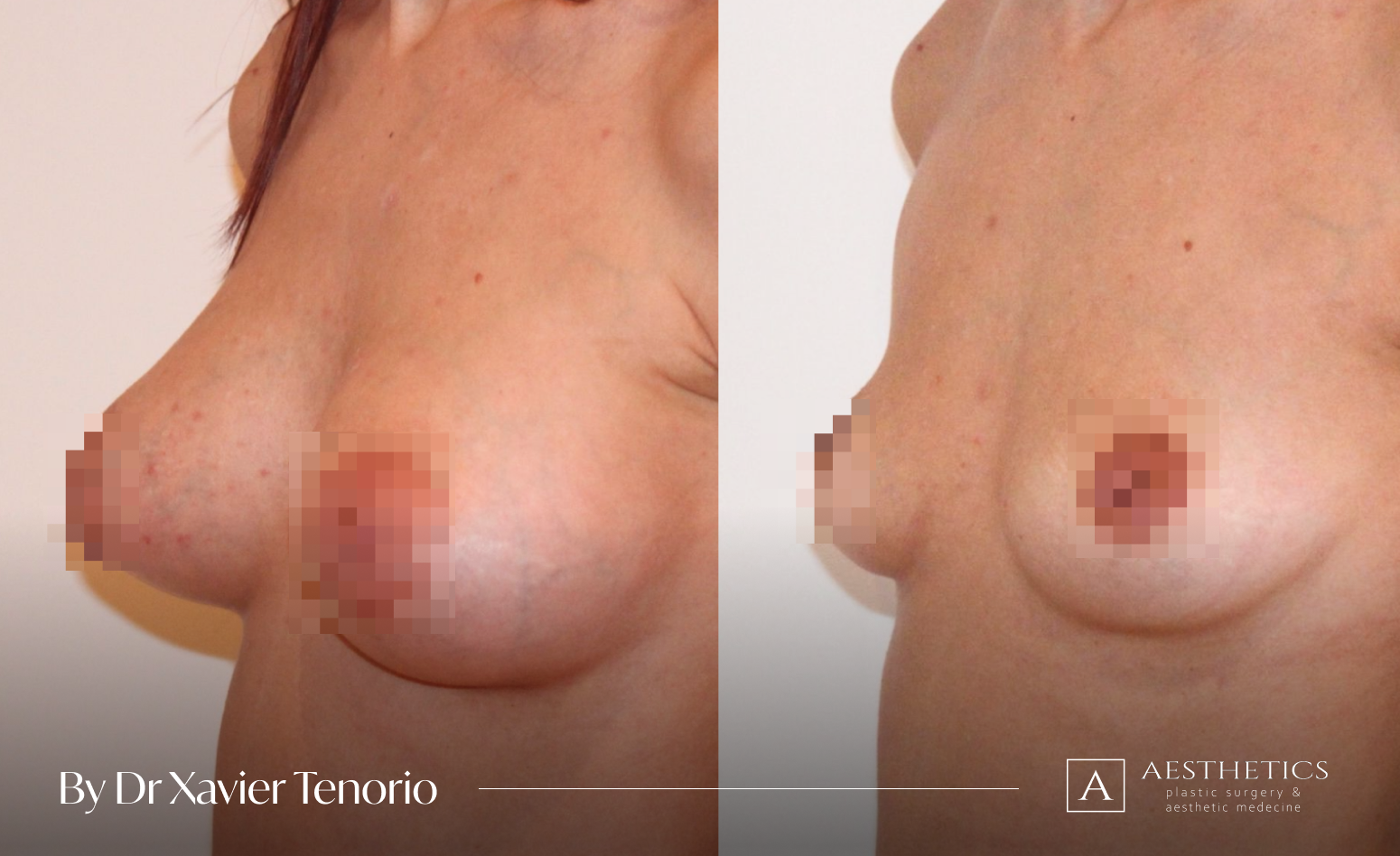
The result for our customers
Book a FREE 3D consultation and we’ll show you the results of our customers who are close to your personal case.
Fill the form to get more before and after photos
A 5-year wait for breast augmentation?
Dr Xavier Tenorio, FMH in plastic surgery and aesthetic medicine, says: “Breast augmentation is the second most common surgical procedure performed in my practice in Geneva, preceded by liposuction (lipoaspiration or fat transplantation).
As a Geneva plastic surgeon with a passion for aesthetic breast enhancement by breast lift, breast lipofilling or prostheses, I have treated a large number of patients in Geneva who consult me for a variety of aesthetic reasons to have their breasts enhanced, always including problems related to the volume and shape of the breasts.
Most of these problems are the result of various situations such as lack of development in adolescence, excessive reduction in volume after pregnancy, abnormal development with asymmetrical malformations such as tuberous or restrictive breasts, deformities or reconstruction as part of cancer treatment in medicine. The smile on my patients’ faces after a successful operation is one of my greatest gifts”.
Breast augmentation using prostheses or fat transplantation?
The aim of breast augmentation surgery is to obtain the desired breast size and volume. There are several ways of achieving this:
- By adding breast implants or prostheses, using the most appropriate incision on the areola, sub-breast fold or armpit.
By fat grafting or transplanting fat taken from another part of the body, also known as breast lipofilling. - Modern implants are filled with cohesive silicone or saline solution, and each prosthesis is the result of the latest medical technology. Their shape and size can be chosen according to the patient’s needs and morphology, with little or no interference with future breastfeeding and mammogram checks.
- The shape of the implant can be round or anatomical. We prefer MOTIVA TrueFix anatomical implants, which have the technology to prevent rotation, movement and displacement of the prosthesis. Ideal for patients looking for a natural result, for slim patients, and particularly for tuberous breasts.
Breast augmentation is a surgical operation designed to increase the size of the breasts. Women typing breast augmentation Geneva into google will already have some information. The process of this breast surgery involves either using your own fat, known as autologous fat, to restore volume to your breasts, or using breast implants or prostheses with a defined volume to increase your bra cup size. This procedure benefits every woman who wants to improve her appearance by having completely new breasts to boost her self-confidence and femininity.
You don’t type Geneva breast augmentation on the Internet by chance. Most women opt for a breast lift or breast augmentation to restore their breasts after pregnancy or ageing, but breast augmentation surgery is also essential for many other reasons, such as breast reconstruction after a mastectomy. Women not only regain much of their femininity, but also put a smile back on their face. Breast augmentation requires a qualified and experienced surgeon and is carried out in a surgical centre under anaesthetic. Most of the time, you can go home a few hours after breast surgery. Are you looking for safe, professional breast augmentation in Geneva, Switzerland, using implants or lipofilling? You’ll find all the information you need on this site. As we explained above
Breast lifting can be combined with breast augmentation with prosthesis or with fat transplantation.
The aim of this article is to provide you with all the information you need about this surgical procedure, bearing in mind that it does not replace a consultation with our surgeons in Geneva. Contact us for any information you may need about breast augmentation surgery in Geneva. Our website is intended to be helpful but cannot replace a medical consultation in Geneva.
We are also here to help you with your breast augmentation! Geneva is a city where people often talk about cosmetic surgery, and we should point out that, with the exception of certain reconstruction operations, breast implants are not covered by any health insurance in Switzerland. Contact us for more information about breast augmentation!
Anaesthesia for breast augmentation. Local, sedation or general anaesthetic?
At Aesthetics Clinic, we put your comfort and safety first during every surgical procedure. For breast augmentation, we offer several anaesthesia options tailored to your individual needs: local anaesthesia, sedation and general anaesthesia. Here’s an overview of each type of anaesthetic to help you understand what you can expect.
Local anaesthesia
Local anaesthesia involves the injection of an anaesthetic directly into the surgical area to numb the region.
Benefits:
Consciousness Maintained. You remain awake and aware throughout the procedure, although you feel no pain in the treated area.
Rapid recovery. Patients generally recover more quickly after a local anaesthetic, with less risk of nausea and other side effects.
Less Risk. Reduces the risks associated with general anaesthesia.
Ideal for. Minor or less invasive procedures. Patients who prefer to avoid the risks of general anaesthesia.
Sedation
Sedation uses drugs to relax you and make you drowsy, but you may remain partially conscious. It is often combined with a local anaesthetic.
Benefits.
Reduced anxiety. You will be relaxed and calm, with little or no memory of the procedure.
Increased comfort. Provides a good balance between comfort and minimal awareness.
Relatively Fast Recovery. Generally faster than general anaesthesia.
Ideal for patients anxious about remaining fully awake. Moderately invasive breast augmentation procedures.
General anaesthesia
General anaesthesia renders you completely unconscious for the duration of the operation. It is administered by a qualified anaesthetist who monitors your condition throughout the procedure.
Total unconsciousness. You will feel no pain and remember nothing of the procedure.
Safety and Control. Allows complete control of pain and sensation, ensuring a discomfort-free procedure.
Suitable for complex procedures. Ideal for longer or more complex surgical procedures.
Ideal for more invasive breast augmentations. Patients who prefer not to feel or remember the procedure.
Choosing the Right Type of Anaesthesia
Factors to consider:
Type of Procedure. The complexity and duration of the procedure will influence the choice of anaesthetic.
Personal Preferences. Your comfort and tolerance of anaesthesia play a crucial role.
General health. Certain medical conditions may require a specific type of anaesthetic.
Pre-operative consultation.
During your pre-operative consultation at Aesthetics Clinic, our medical team will discuss your anaesthetic options in detail. We will assess your general health, personal preferences and the specifics of your planned procedure to recommend the most appropriate anaesthetic for you.
For more information about anaesthesia for breast augmentation or to schedule a consultation, please contact us at [clinic contact information] or visit our website at [clinic website]. We are here to ensure you have a safe, comfortable and satisfying experience.
Recovery after breast augmentation
Your recovery and convalescence after breast augmentation
Recovery time after breast augmentation surgery is around 6 to 8 weeks, and progress is visible day by day. After surgery, you will rest in a recovery room, slowly waking up from the anaesthetic. You will feel dizzy and may experience some pain. If the implants are placed under your pectoral muscle, you may also feel tense. Week by week, as the muscles relax and loosen, the pain will diminish and become more manageable. Recovery from breast augmentation begins immediately after surgery and within a few hours of leaving the operating theatre, you will begin to feel less sore and free to go home.
After breast augmentation, it is important to take time to recover properly. For the first few days after surgery, you will probably feel tired, achy and a little nauseous. You should plan to spend at least a few days resting at home. Dr Xavier Tenorio will provide you with specific instructions on post-operative care. It is important to follow these instructions carefully to avoid any complications and speed up the healing process. You should avoid strenuous activity for the first few weeks after surgery. This includes physical exercise, heavy housework and sexual activity. You should also avoid wearing tight bras during this period.
For the first few weeks, you may experience mild pain and discomfort, as well as swelling and bruising. Dr Xavier Tenorio will probably prescribe painkillers to help you feel more comfortable. Make sure you follow Dr. Tenorio’s instructions for aftercare and follow-up appointments. This will ensure that you recover properly and are happy with the results of your breast augmentation in Geneva with a smile on your face!
Recovery from any operation or surgery is vital and, of course, a breast implant, reduction or even a breast lift is no less important. Not only will you need to recover from the anaesthetic process, but you’ll also need to take it easy and look after your new body!
How quickly can you recover from breast augmentation surgery?
Every recovery depends on you and your body! Certain factors can increase or reduce recovery time, such as nutritional intake, medical history or general adherence to the surgical procedure. Normally, most patients return to their usual activities after 4 to 6 weeks, but it is important to remember that the muscles and implants will not begin to relax and stabilise until 2 to 3 months after the operation.
How can I improve recovery after breast augmentation surgery?
Everyone recovers differently, so we recommend that you listen to your body. However, there are a few rules to follow for a correct and rapid recovery. Just before and after the operation, avoid anticoagulant or anti-inflammatory drugs (aspirin or ibuprofen), fats rich in omega 3, vitamin E and alcohol, as these can cause bruising and swelling. Start massaging the implants every day 2 weeks after plastic surgery. Massages should be performed more comfortably in the shower with warm water to help the muscle relax. Sleeping on your back keeps the breast implant in place and helps the tissues to heal properly. Sleeping with your head elevated for a month helps to reduce swelling. Throughout the recovery process, it is very important to stay hydrated and eat foods rich in vitamins and fibre.
Is recovery painful?
Recovery from breast augmentation surgery depends on the individual’s pain threshold, reaction and general state of health. Variables such as the type of incision, the location, type and size of the implant influence the pain that can occur. Subpectoral positions (below the muscle) are more painful than subglandular positions (above the muscle). If the implant is large or if the initial size of the breast is small, recovery after the operation is generally more intense. You will be given antibiotics to aid recovery and prevent infection. In the days that follow, most people can switch to pain medication. The pain should diminish day by day. The first week will be the most uncomfortable, then slowly but surely you will start to feel much better.
What should I have/buy at home during my recovery?
Before you begin your plastic surgery, it would be wise for you to make sure you have everything you need at home for a better recovery. Prepare clothing and blouses that are not restrictive so that you feel comfortable. Straws are essential so that you can drink liquids in bed, and baby wipes are useful to make cleaning easier on days when you can’t have a shower. Your doctor will provide you with a bra suitable for the post-operative period, but you should have a soft, non-wired bra at home that you can wear when you remove the bra after the operation.
Take good care of yourself during your recovery.
The food we give our bodies is very important. During your recovery, eat protein-rich foods such as chicken and eggs and, of course, the following foods are essential in your kitchen:- Fibre-rich foods such as nuts and seeds (cashews, almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds and sunflower seeds) help skin tissue to heal and regenerate. – Fruits such as bananas, apples, oranges, kiwis and pineapples help to boost your immune system.Having someone at home after the operation is important in case you start to feel ill or dizzy and, in general, so that they can help you with anything you may need.
Necessary visits with your doctor
After the operation, Dr Xavier Tenorio, your cosmetic surgeon, will arrange a series of appointments with you to review your progress. The first of these visits will take place after one week. After the first visit, three further visits are usually scheduled during the first year (further visits will be scheduled if necessary or if complications arise).
Recovery time after breast implant surgery
First few hours:
When Dr Xavier Tenorio your cosmetic surgeon in charge of your breast augmentation deems it appropriate to discharge you, you will be able to go home. You will be given antibiotics, the special post-operative bra you will wear for the next four weeks and a personalised programme to follow.
First week:
Stay in bed for as long as possible, and shower after 36 hours. You can remove your bra, but keep the gauze pads and straps in place. Make sure someone else is at home with you in case you start to feel sick, weak or dizzy. Dry the area well and put the bra back on after showering. It is advisable to sleep on your back with your head elevated to reduce swelling. Keep your post-operative bra on day and night, at least 23 hours a day.
First week after plastic surgery:
This is the time for the post-operative consultation with Dr Xavier Tenorio FMH in plastic surgery and aesthetic medicine in Geneva. If any stitches remain, they will be removed at this time if healing is proceeding as planned. Do not do any work that involves heavy lifting. You can walk, but don’t run and forget the gym for the time being. You may feel a tingling sensation as the nerves begin to heal and grow back. You can return to work if it does not involve heavy lifting or if there are no contraindications that could hinder the healing process.
Risks of breast augmentation
Like many surgical procedures, breast augmentation involves risks and complications that can range from minor to serious. Some of these include:
Complications related to the implants, rupture, capsular retraction, displacement, rotation, etc.
Scarring and tissue deformation around the shape of the implant.
Implant rupture, deflation or leakage.
Changes in implant position.
Changes in breast sensation.
Infection.
Hematoma / immediate and delayed seroma
Immune reactions
Cancer of capsular origin (very rare)
First consultation
with 3D simulation
in Geneva, Gstaad and Montreux
Fill in the form to request a free consultation
Go to formFirst consultation
with 3D simulation
in Geneva, Gstaad and Montreux
First consultation
with 3D simulation
in Geneva, Gstaad and Montreux!
Booking
Fill in the form to request the free consultation
Go to FormType of breast augmentation and treatment methods.
All the breast surgery operations on offer
Breast augmentation with implants
Guide to Breast Implants at Aesthetics Clinic Geneva
We understand that choosing the right breast implants is an important decision. We offer both round and anatomical (teardrop-shaped) implants to suit a variety of aesthetic goals and body types. Here’s a detailed look at each option to help you make an informed choice.
Anatomical (Gout Shaped) Breast Implants
Anatomical implants mimic the natural shape of the breast, with more volume at the bottom and a tapered top, creating a drop-shaped silhouette.
Benefits
Natural Appearance Provides a more natural contour, particularly beneficial for those with little natural breast tissue.
Ideal for thin women with small starting volumes. Often used in breast reconstruction to achieve a natural shape after surgery.
Customisable Available in different heights, widths and projections to suit individual proportions.
Micro-textured surface and fixation system. These implants have a micro-textured surface and a fixation system (Motiva TrueFix) to prevent rotation in the breast pocket, ensuring that the shape remains constant.
Round Breast Implants
Round breast implants have a symmetrical spherical shape that enhances breast volume and cleavage.
Benefits Increased volume, ideal for those looking for significant volume in the upper part of the breast. Less risk of rotation, their shape remains constant if the implant rotates. Versatility, suitable for a variety of body types and aesthetic goals.
Smooth Surface These implants move more naturally in the breast, providing a realistic feel. Textured and microtextured surface. Designed to adhere to surrounding tissue, reducing the risk of displacement.
Comparison of Round and Anatomical Implants
Appearance
Round Implants Provide pronounced cleavage and volume, especially in the upper breast.
Anatomical Implants Offer a subtle, natural slope that resembles the natural shape of the breast.
Sensation
Both types can offer a natural feel, with texture and placement influencing the overall sensation. Smooth round implants can more closely mimic the natural movement of the breast.
Risks and Considerations
Round Implants Less concern about rotation due to their symmetrical shape but more risk of making folds that may be palpable or visible.
Anatomical implants Less potential risk of rotation with the TruFix system,
Cost
Anatomical implants are generally more expensive than round implants due to their specialised design.
Making the Right Choice
Personal Goals , For pronounced cleavage and volume, round implants may be the best choice. For subtle, natural enhancement, anatomical implants are often preferred.
Body Type, Our surgeons will take into account your body type, breast width and natural breast tissue to recommend the most appropriate implant type.
Consultation at Aesthetics Clinic Geneva
We believe in personalised care and in-depth consultations. During your visit, our board-certified plastic surgeons will discuss your aesthetic goals, assess your body type and address any concerns you may have. This comprehensive approach ensures that you receive the most appropriate and satisfying treatment.
To schedule a consultation or learn more about breast implants at Clinique Esthétique de Genève, please contact us at [clinic contact information] or visit our website at [clinic website]. We are here to help you achieve the look you desire with confidence and care.
Breast augmentation by fat transfer
Moderate breast augmentation using fat transfer, which can be removed by liposuction from one or more areas of the body, is another breast augmentation option. This technique, widely used for total breast reconstruction after cancer, is gaining increasing acceptance in aesthetic plastic surgery.
Breast lift
In general, breasts become ptotic (sagging) due to a normal increase in volume during pregnancy and breastfeeding, followed by significant atrophy of the breast tissue in the months following breastfeeding. Women who have lost a significant amount of weight, particularly obese patients who have successfully dieted, exercised or undergone weight loss surgery, may also lose mammary gland tissue, leading to the formation of Ptotic breasts. Finally, breasts can be reduced in size and projection as a result of the normal ageing process.
Also known as mastopexy, breast lifting is a surgical procedure used to lift and reshape breasts that have become less firm, often as a result of pregnancy, breastfeeding, weight loss or gravity.

Round implants
They have been used for a very long time, are very safe and give good results, but in slim patients these implants produce round upper poles, which are less natural than a progressive or ‘décolté’ upper pole.

Anatomical implants
They were originally designed for breast reconstruction. Anatomical implants already have the shape of a breast. They have a thinner upper pole and give more projection in the lower pole.

Composite breast augmentation
Composite breast augmentation is a technique that combines the use of implants and fat transfer to increase the size of the breasts. This method is ideal for women who do not have enough breast tissue to cover an implant.
Recovery
Pain may occur immediately after the operation. They are generally well tolerated and treated with painkillers for a few days. In some cases, patients feel a certain amount of tension in the area where the implants have been placed. The oedema (swelling) only lasts a few days.
The first dressing is changed after 24 to 48 hours and replaced by a lighter dressing. Two or three days later, it is again replaced by a sports bra for 4 weeks, day and night.
Working time
A recovery period of 8 to 10 days is recommended. Full physical and sporting activities can be resumed after two months.
Results
Patients are very satisfied with the immediate result, but the shape improves with time and the final result is always appreciated once the convalescence is over. Beyond the aesthetic improvement, the psychological impact is also very strong because it is really a new life that begins with a new femininity that will be with you every day.
Questions and answers Breast augmentation
Breast augmentation is generally performed under general anaesthetic in Geneva, although in some cases it can be avoided by sedation combined with a nerve block.
Hospitalisation: A single day’s hospitalisation in Geneva is generally sufficient. A prosthesis, whether filled with a cohesive solution of silicone or serum, has a lifespan that cannot be accurately estimated. A priori, a quality implant does not theoretically have a limited lifespan. There is no expiry date after which the implant must be changed. So, in the absence of complications, the implant can be kept for as long as the patient wishes. Breast augmentation, although performed primarily for aesthetic reasons, is a genuine surgical procedure, which carries risks like any other medical procedure (however minor). It is important to distinguish between complications related to anaesthesia and those related to breast augmentation surgery in Geneva.
Concerning anaesthesia: The anaesthetist will explain the risks and answer the patient’s questions during a pre-operative consultation. Current technology means that anaesthesia can be performed in the safest possible conditions for both the patient and the surgical team.
Concerning breast augmentation surgery: The choice of a qualified surgeon, trained in this type of surgery, limits the risks as much as possible, without however eliminating them completely. Dr Xavier Tenorio offers world-renowned expertise in breast augmentation.
Rare but possible complications: Infection requiring antibiotic treatment and sometimes surgical drainage. Formation of a haematoma requiring drainage (evacuation). Decreased sensitivity, particularly in the nipple area, but normal sensitivity generally returns within 6 to 18 months. Problems with the healing process are observed in heavy smokers and diabetic patients. Hypertrophic scars and even keloids may be found in the scars of patients with an unfavourable healing process.
Specific risks of Dual Plan breast implants: These can be divided into three groups depending on the nature of the implant filler. Flods, which can sometimes be observed under the skin, are more commonly associated with saline implants in a retroglandular position. A capsular formation appears around an implant. It consists of a fibrous membrane that envelops any foreign body. In some cases, this membrane thickens, shrinks and forms a true fibrous capsule around the implant, which can distort the shape of the breast and be painful. The frequency of this complication cannot be estimated in general terms, as it varies according to the indication for surgery, the type of implant and the procedure.
Treatment consists of releasing the tension around the implant by incising the capsule (it seems that textured implants and those placed behind the muscle have a lower overall rate of capsule formation). Rupture and deflation can occur as a result of deterioration of the implant shell, violent trauma or a manufacturing defect.Rupture of a cohesive silicone implant may go unnoticed after implant placement and breast augmentation. The cohesive silicone remains confined in the capsule around the implant and causes only slight deformation. However, rupture of the capsule following perforation can result in silicone leakage with potential granuloma formation.rupture of a saline implant results in rapid deflation. In these cases, the implant must be replaced.
Can cancer be monitored with implants? Clinical monitoring is straightforward when the implants are placed behind the mammary gland. However, the presence of an implant can alter the ability of X-rays to detect breast cancer. For this reason, people with implants should tell their radiologist, who may use specific, adapted methods (ultrasound, digital mammography).
To sum up, there is no reason to overestimate the risks, but it is important to realise that any surgical operation, however apparently simple, always involves a small element of risk. Perhaps this reading will raise new questions, which our reception team will be ready to answer at our clinic in Geneva, Switzerland.
Breast surgery in Geneva
Geneva is an excellent place for breast augmentation surgery. The city has reputable facilities and board-certified surgeons with years of experience in the field. These experts offer consultations and medical assessments to help identify the ideal type of implant for the condition of your breasts. These sessions are crucial, as this is the time to decide on the ideal type of incision based on the surgeon’s and patient’s preferences. Breast augmentation in Geneva is generally an in-patient procedure. The procedure itself takes about 1 hour, but surgeons need time to monitor progress before discharging you. You will need to stay in Geneva until Dr Xavier Tenorio gives you permission to go home. The cost of breast augmentation in Geneva varies according to the individual case. But bear in mind that the price could be higher or lower depending on your preferences, the level of expertise required and many other factors.
Choice of breast prostheses
Choosing the size and shape of your silicone breast implants is a very personal decision. We’ll suggest what’s best for you based on what you want from your operation and the proportions of your body, but choosing exactly the shape you want your breasts to be may seem like a daunting prospect, but it doesn’t have to be.
Breast Implant Size Guide
What is the most common breast implant size?
To determine the right breast implant size for you, you need to choose the implant shape, volume and profile that’s right for your unique body. Breast augmentation professionals work in cubic centilitres (cc), and as bra manufacturers only use cup sizes, it’s important to know which breast implant size is right for you based on your bra size.
- As a general rule, the most common breast implant size is between 300 and 500 cm3.
- 400cc implants are generally the most common.
- Implants in the 300cc to 360cc range are generally sufficient to give women a fuller shape without significantly altering their figure.
If you are considering breast augmentation, you will need to take into account a number of factors, such as your height and weight, the current shape and size of your breasts, and the characteristics of your chest wall and breast tissue.
What are the smallest breast implant sizes?
Breast implants are generally around 125 cm3 in size, but in rare cases can be as small as 80 cm3, offering some of the following benefits:Smaller implants can improve the appearance of breast augmentation, as a more subtle breast implant can provide an improvement without radically changing the shape. Smaller breast implants generally mean a smaller scar, which greatly reduces the risk of breast-related problems, such as back or neck pain. Smaller breast implants generally mean a smaller scar, which greatly reduces the risk of breast-related problems such as back or neck pain.Smaller breast implants are suitable for women who are looking for a more natural-looking breast augmentation or who want smaller breasts for practical reasons, such as exercise or finding the right bra size.
What are the largest breast implant sizes?
Breast augmentation needs vary from patient to patient, and the largest implants are generally considered to be 800 cm3 or more. The largest size of breast implant approved by the Public Health Authority is up to 800cm3, which covers silicone gel breast implants and saline breast implant shells, the latter being more common in larger breast augmentation procedures, as saline implants can be inserted during the procedure and filled to the desired size afterwards.
What is the average size of a breast implant?
The most common implant size varies between 200 and 850 cm3. As breast implants are available in almost any size and shape, the sizing process is essential and must take into account individual proportions, such as shoulder width, ribcage shape, hip width, breast width and waist-to-hip circumference ratio.
What is the best way to compare breast implant sizes ?
To determine the breast implant size that’s right for you, there are a few things you need to consider. As bra manufacturers don’t work in cubic centilitres (cc), you need to understand the general rule of thumb for increasing your cup size according to your breast implants.It generally takes around 200 cc to increase your breast size by one cup size, but this depends on the bras you choose and how the manufacturer determines cup sizes. When it comes to knowing how much you want to increase your cup size, the following proportional measurements can help you make your decision: How to choose the right breast implant size for you There are many factors to consider when choosing the right breast implant size for you. It’s always your choice, but here are some factors to consider:Don’t think in terms of your bra cup sizeWe’ve already shown you how significant the increase can be when you go up a cup size, but it’s not an exact science because of the bra manufacturer. Instead of basing your goals on the bra size you’d like to wear, patients should be encouraged to understand the cc measurement and try a number of different profiles and sizes that will have a better impact on the final result.Consider the type of implants on offerBreast augmentation comes in different profiles and shapes, the most common being the teardrop or round shape. A teardrop-shaped implant corresponds to the natural shape of the breast, while round implants have a rounded shape. Understanding what’s best for your body will help you make the right decision first time.Get to know your body betterAt your initial consultation, you’ll be asked a number of questions based on your expectations. To choose the ideal breast implant size, you need to familiarise yourself with your body. Measurements will be taken, including your build, weight, height, shoulder width and current breast size, all of which will be taken into account when choosing the right breast implant.Think about your lifestyleBreast implants are there to improve your life and your body. They should not prevent you from living the life you want. By telling your doctor about all your hobbies, you can ensure that the implants you choose will not prevent you from carrying out your daily activities. Many sportswomen have undergone breast augmentation or reduction without any discomfort or difficulty.Know your “why “Some people choose breast augmentation to enhance their breasts, but others don’t want to draw more attention to themselves. People choose breast implants for a number of reasons. Whether you want to feel more confident on the beach or you want people to treat you with more respect, the right size breast implant will give you confidence and credibility in the right way.
Back to sport
Breast augmentation is an essential procedure for many aesthetic and medical reasons, so it’s important to find a reputable Swiss clinic that offers low-risk options and top-quality services like the Aesthetics Clinic. In this way, you can achieve the best possible results with the minimum of complications or risks, and resuming sport in this sense is a big question.Resuming sport after breast augmentation depends on the type of surgery undergone and the patient’s state of recovery.
In general, it is recommended not to engage in strenuous physical exercise for the first few weeks after surgery to avoid excessive strain on the breast tissue.Recovery time varies according to the type of surgery. If the patient has undergone breast augmentation with an implant, she should be able to resume light physical activity after about 4 to 6 weeks, but should avoid exercise that strains the pectoral muscles for about 12 weeks. If the patient has undergone breast augmentation by lipofilling or fat transfer, she can resume light physical activity after about 2 to 4 weeks, but should avoid chest exercises for about 4 weeks.It is important to discuss specific recommendations for resuming sport after breast augmentation with Dr Xavier Tenorio, as each case is unique.
It is also important to start slowly and progress gradually to avoid any pain or complications. At the Aesthetics clinic you’ll also find expert advice on rhinoplasty, eyelid surgery, laser treatments, internal surgery and facial injections with hyaluronic acid.After breast surgery, such as breast augmentation, breast reduction, breast lift or breast reconstruction, it’s generally advisable to move around quickly and increase your activity. However, when you are resting, the way you position yourself can promote better healing. Dr Xavier Tenorio, an internationally renowned plastic surgeon based in Geneva, gives you some valuable advice on this subject. Sleeping on your back after breast augmentationParticularly in the first few weeks after the operation, sleeping on your back, usually wearing a surgical bra, allows the breasts to heal in a more comfortable and desirable position.
Sleeping on your stomach or on your side can put pressure on the breasts, including the implants, and can lead to unwanted early displacement of your implants. If you are accustomed to sleeping on your stomach or side, Dr Xavier Tenorio of Geneva suggests that you practise sleeping on your back in the weeks leading up to the operation, and patients can usually safely return to their preferred sleeping style four to six weeks after the operation. Some women may find that their sleep preferences have changed after breast surgery. For example, some women with breast implants may find it more comfortable to sleep on their side rather than on their stomach.Use several pillows to elevate your headPlacing your head slightly above your body while you sleep serves several functions simultaneously. Firstly, if two or three pillows support your neck, it will be more difficult for you to lie on your side or stomach during the night, even unconsciously. Secondly, this elevated position can be more comfortable because it reduces swelling. Take steps to promote better sleep Your body does much of its healing while you sleep.
So it’s important to make getting a good night’s sleep a priority. To make sure you fall asleep more easily, avoid drinks and foods containing caffeine, such as coffee, tea, soft drinks and chocolate, the night before you go to bed. Set the thermostat to a temperature at which you are most comfortable and use fresh sheets. Don’t look at your phone or the television in the hour before you go to bed, as the blue light emanating from these devices can interfere with sleep.
What is breast hypoplasia?
Breast hypoplasia is what women most often refer to as “no breasts”. In more medical terms, it refers to breasts that are underdeveloped or not developed at all. For all women, the breast is a relational organ, a mirror of their femininity and an element strongly associated with motherhood. Rationally speaking, this could be nothing serious and, from some points of view, even attractive, but for the female figure, not being able to enjoy breasts that fall within the most classic canons is generally a source of great psychological discomfort.
Causes of hypoplasia
First of all, it is important to stress that this condition does not involve any health problems. There are generally three main causes
- genetics
- breast-feeding
- significant weight loss.
As far as family history is concerned, the problem is generally stable in the post-pubertal phase, i.e. around the age of 18-20, when the period of development comes to an end. Breastfeeding can also compromise the volume of the breast, especially if it is small to begin with, leading in most cases to emptying, especially of the upper pole. Even if you decide to go on a diet, it really is essential to proceed gradually to prevent the mammary gland from shrinking excessively, also compromising the elasticity and tone of the skin, which runs the risk of becoming an “empty sack”, sometimes wrinkled.
The cosmetic surgery solution
The remedy is simple, although plastic surgery is necessary.
Breast hypoplasia can in fact be corrected by a breast augmentation procedure, which aims to give volume and shape to ‘flat’ breasts, guaranteeing naturalness and harmony while respecting physical conformity. Breast augmentation is achieved through the use of specific breast implants which, positioned – in most cases – behind the pectoralis major muscle, will restore the desired femininity.
Ask for your breast augmentation consultation!